**1. Cylinder Inspection and Maintenance**
1.1 Inspect the cylinder for roundness and cylindricity to assess wear. If the wear exceeds acceptable limits, the cylinder should be repaired or replaced.
1.2 The roundness and cylindricity of the cylinder must conform to the values specified in Table 5.
| Cylinder Diameter | Max Wear (Roundness) | Max Wear (Cylindricity) | |------------------|----------------------|--------------------------| | >200~250 | 0.40 | 0.25 | | >250~300 | 0.45 | 0.30 | | >300~350 | 0.50 | 0.35 | | >350~400 | 0.55 | 0.40 | | >400~450 | 0.60 | 0.45 | | >450~500 | 0.65 | 0.50 |
1.3 The inner surface of the cylinder must be free from cracks, blisters, scratches, or grooves. The surface roughness should not exceed 1.6 µm.
1.4 After hammering, the cylinder diameter should not increase by more than 2% of its original size, and the wall thickness should not fall below 1/12 of the original thickness.
1.5 The water jacket of the cylinder must be free from cracks or leaks.
**2. Crankshaft, Connecting Rod, and Bearing Bush**
2.1 Crankshaft
2.1.1 Measure the wear on the main journals and crankpins. If necessary, repair using metal brushing or spraying techniques.
2.1.2 The allowable wear values for the main journal and crankpin are as per Table 6.
| Journal Diameter | Spindle Neck Roundness | Spindle Neck Cylindricity | Crank Neck Roundness | Crank Neck Cylindricity | |------------------|------------------------|---------------------------|-----------------------|-------------------------| | ≤80 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | | 81~180 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | | 181~270 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
2.1.3 The maximum reduction in the journal diameter should not exceed 3% of the original diameter.
2.1.4 Scratches or grooves on the journal should not cover more than 2% of the area, with a depth not exceeding 0.10 mm. These areas should be ground and repaired.
2.1.5 If non-destructive testing or magnifying glass inspection reveals cracks, the crankshaft must be replaced.
2.1.6 The parallelism between the crankshaft axis and the reference axis should be between 0.20–0.30 mm.
2.1.7 The straightness of the crankshaft should be within Φ0.05 mm.
2.2 Connecting Rod
2.2.1 The small pin hole axis of the connecting rod must be parallel to the reference axis within 0.3 mm.
2.2.2 Bending or torsion deformation can be corrected using a connecting rod corrector. If it still doesn’t meet standards, replace the part.
2.2.3 The verticality of the connecting rod’s big and small pin holes should be within 0.50 mm.
2.3 Bearing Bush
2.3.1 The bearing alloy must adhere well to the bush shell without cracks, pores, or delamination.
2.3.2 The contact area between the bearing bush and housing should be at least 40–50%, and no gasket should be used between them.
2.3.3 The bearing bush should make point contact with the journal, with a contact angle of 60–90° and at least 2–3 points per cm².
2.3.4 The radial clearance between the bearing bush and journal should be 1‰ of the journal diameter.
**3. Piston and Piston Ring**
3.1 The piston and piston ring surfaces should be smooth and free from cracks, blisters, or scars.
3.2 The installation clearance and allowable wear for the piston and cylinder are shown in Table 7.
3.3 The piston ring must have sufficient spring force, with at least 60% of the circumference in contact with the cylinder wall.
3.4 The piston rings in the groove should be staggered by 120° from each other.
3.5 The clearance, backlash, and maximum wear for the piston ring are listed in Table 8.
| Cylinder Diameter | Installation Gap | Backlash | Max Wear | Side Clearance | |------------------|------------------|----------|----------|----------------| | >200~250 | 1.00 | 0.05–0.07| 4.00 | 0.20 | | >250~300 | 1.20 | 0.06–0.09| 4.50 | 0.20 | | >300~350 | 1.40 | 0.06–0.09| 5.00 | 0.20 | | >350~400 | 1.60 | 0.07–0.10| 5.50 | 0.20 | | >400~450 | 1.80 | 0.07–0.10| 6.00 | 0.20 | | >450~500 | 2.00 | 0.09–0.12| 6.50 | 0.20 |
**4. Piston Rod**
4.1 The maximum wear of the piston rod should not exceed 0.05–0.07 times the diameter (D).
4.2 The straightness of the piston rod should be within Φ0.10 mm.
**5. Valve and Seat**
5.1 The valve plate and seat joint surface should be free from etching, scratches, or other defects.
5.2 The valve plate and seat must form a tight seal, with no leakage after a 5-minute kerosene test.
5.3 The valve spring must have sufficient force, and all springs of the same valve should have the same free height.
**6. Crosshead and Guide**
| Crosshead Diameter | Clearance | |--------------------|-----------------| | 80–120 | 0.20–0.24 | | >120–180 | 0.24–0.29 | | >180–260 | 0.29–0.34 |
6.1 The crosshead must be free from cracks or other structural defects.
6.2 The maximum wear on the crosshead pin should not exceed 0.50 mm.
6.3 The clearance between the crosshead and guide rail should comply with Table 9.
6.4 The clearance between the crosshead pin and bushing should be 0.03–0.06 mm.
6.5 The contact area between the crosshead and guide rail should be at least 60%, with evenly distributed contact points.
**7. Adjustment Requirements**
7.1 The clearance at both ends of the piston stroke should be 1.50–2.00 mm.
7.2 Valve position adjustment steps:
a. Rotate the crankshaft so that it slightly passes the front dead center.
b. Position the eccentric at the highest point vertically.
c. Place the valve centrally over the cylinder seat.
d. Fix the entire valve transmission mechanism at this position.
**Editor: Hardware Business Network Information Center**
**Source: http://news.chinawj.com.cn**
Shift fork normally applied in the transmissions, its function is help to slide gears into or out of engagement with other gears in order to change from one gear ratio to another in a manual transmission.
QFAP supply various kinds of shift forks to all over the world, main of our customers are digger/excavators manufacturers, lawn mower manufacturers, truck transmission factories and construction machinery companies.
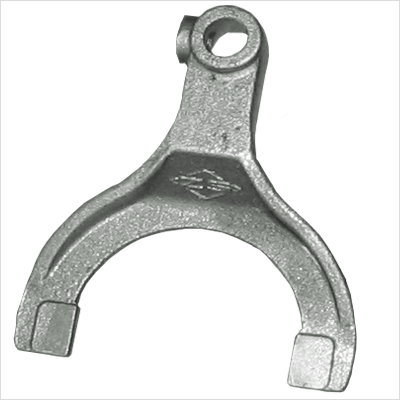
Materials: carbon steel castings, stainless steel castings, alloys steel castings, aluminum die castings, forging steel castings, etc.
Surface treatment: painting, zinc plating, passivation, nickel plating, anodizing, polishing, etc.
Heat treatment: according to customer`s requirement.
QFAP have specialized in producing high precision Agriculture Parts more than 10years, Because of the long term cooperation, we could supply our customers not only the products but also our recommendation on the designs to saving costs.
Shift Fork,Shift Fork Gear,Transmission Shift Fork,Reverse Shift Fork
SHAOXING QIFENG AUTO PARTS CO., LTD. , https://www.sxqfap.com